Do you know about protein Biochemistry ? come, today we are going to read about protein biochemistry. protein is derived form the Greek word “PROTEIOS”. Which means of “Primary Important” father of protein is called J.J. Berzelius. protein is a Bio molecule which is made up Carbone Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphate group also present. we have read in protein Biochemistry.
Protein biochemistry
Definition –
Proteins are Bio macromolecular polymer composed of Amino acid as basic unit linked by peptide bond. or when two or more then two molecule amino acid connect by peptide bond, is called proteins.
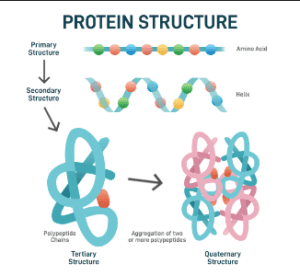
what is Bio molecule ?
molecule which is present living system. It is called bio molecule.
For more: Downy Mildew: Identification, Cause, Precaution And Treatment
What is amino Acid ?
Amino acid is a organic compound which is made two group. (1) Amino group (NH3) and (2) carboxylic Group.
What is Peptide Bond ?
Peptide bond is a covalent bond that from between amino group and carboxylic group. its make proteins channel
Chemical Composition of Proteins
Protein Chemical compose in five Element. (1) Carbon- C is found between 50-55 %. (2) Hydrogen– H is found between 6-8%. (3) Oxygen– O is found between 20-23%. (4) Nitrogen– N is found between 15-18%. (5) Phosphate- P some time found.
Classification of Proteins
(1) On the basis of shape. (2) On the basis of Biological function. (3) On the basis of composition and Solubility.
On the basis of shape
(1) Fibrous Proteins
Fibrous protein looking like a thread type . Ex- Collagen, Keratin, Fibroin, etc..
(2) Globular Protein
Globular Protein is lookin like folding/ spherical/globular type. Globular protein is water soluble. Ex- Enzyme, Antibiotics, Hormones , Pepsin, Trypsin etc…
Also Read: Carbosulfan explained in the best and simplest way in 2024 (Never forget it)
Protein Biochemistry On the basis of Biological function.
(1) Structural Proteins
Structural proteins provided elasticity, strong and support tissues such as skin. Ex- collagen, keratin, and elastin.
(2) Storage Proteins
storage protein are a class of protein whose primary function is to store long period essential nutrient and amino acids for later use. storage protein verry role play to Growth and development. Ex- glycinin (1) Seed storage protein gluten, legumin and vicilin, albumins and Globulins.(2) Ferritin (3) Casein (4) Ovalbumin
(3) Transport Proteins
Transport proteins are integral membrane proteins that facilitate the movement of substances across biological membranes.
(4) Enzymatic Proteins
Enzyme is proteins It work to help speed up chemical reaction in living organism. it have very important role of human body.
(5) Regular Proteins
Regular protein is make to hormones and enzyme to repaired bones and muscles. it is play to important role regarded to getting hurt bones and body muscles.
(6) Protective Proteins
Protective protein protect to come any unwanted thing in your body and It safe you to be any disease. this protein to fight to disease .
(7) Toxic Proteins
It have show toxicity.
Protein Biochemistry On the Basis of composition and Solubility.
(1) Simple Proteins
Simple Protein is composed only amino Acid. do not composed any additional group. is called simple protein Ex- Albumin- Albumin protein is released by lever. It help Blood flowing in the Body very smoothly. it is soluble in water, acid, and base. This protein found egg, Albumin, Serum Albumin etc… Histones- It is soluble in water. It is composed to hemoglobin with reaction to DNA and heme. It is found Wheat etc. Globulins- it is not soluble in pour water but it is soluble in salt water. which is help to stop emission by le
(2) Conjugated Proteins
These have additional conjugated group with amino acids is called conjugated protein. (Amino Acid + nonprotein part = conjugated proteins) Ex-(1) Hemoglobin= heme + globin ( globin is a protein part but heme is a nonprotein part) (2) Casein (casein is called phosphoprotein ) phosphate is a non protein part. (3) Nucleoprotein
Phosphoprotein (casein) –
It is a water in soluble and it have present phosphate.
Nucleoprotein-
It is water in soluble . It have present specific type element. what we call phosphate. phosphate is nonprotein part. Ex- histone
(3) Derived Proteins
These are found by hydrolyzed simple and conjugated proteins. it is called Derived Proteins. Ex -peptide
Conclusion-
We have read this blog protein biochemistry in full detail. How to Work protein, all classification, his nature and with figure.